SOFTWARE
Software
Network structural equation modeling (netSEM) is a data-driven modeling technique that has been developed at the SDLE Research Center and with a public version available as a R software package CRAN. netSEM selects the best relationship between variables based on statistical significance such as adjusted R2 and also rank order models using Akaike Information Criterion (AIC), and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC).
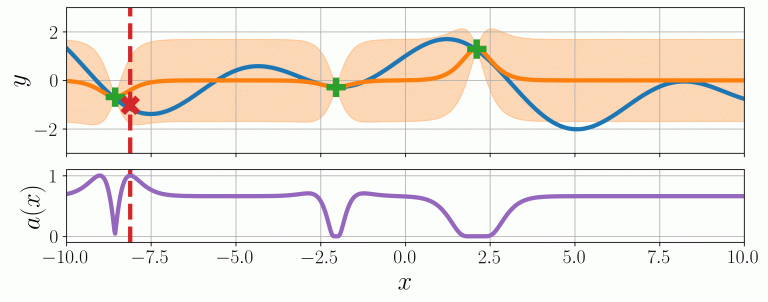
BayesO (pronounced “bayes-o”) is a simple, but essential Bayesian optimization package, written in Python. It is designed to run advanced Bayesian optimization with implementation specific and application-specific modifications as well as to run Bayesian optimization in various applications simply. This package contains codes for several surrogate models such as Gaussian process regression and random forest regression, so that sequential model-based optimization can be implemented.

JaxLayerLumos is open-source transfer-matrix method (TMM) software designed for scientists, engineers, and researchers in optics and photonics. It provides a powerful yet intuitive interface for calculating the reflection and transmission (RT) of light through multi-layer optical structures. By inputting the refractive index, thickness of each layer, and the frequency vector, users can analyze how light interacts with layered materials, including the option to adjust for incidence angles.

litdb is an open-source Python tool for building and searching a personal literature database. It allows users to collect scientific papers and store them locally in a database. Once collected, literature can be searched using semantic and text-based queries, including natural-language queries supported by GPT-style interfaces. Additional features include exporting BibTeX citations, filtering new papers since a given date, and extracting structured data from documents.
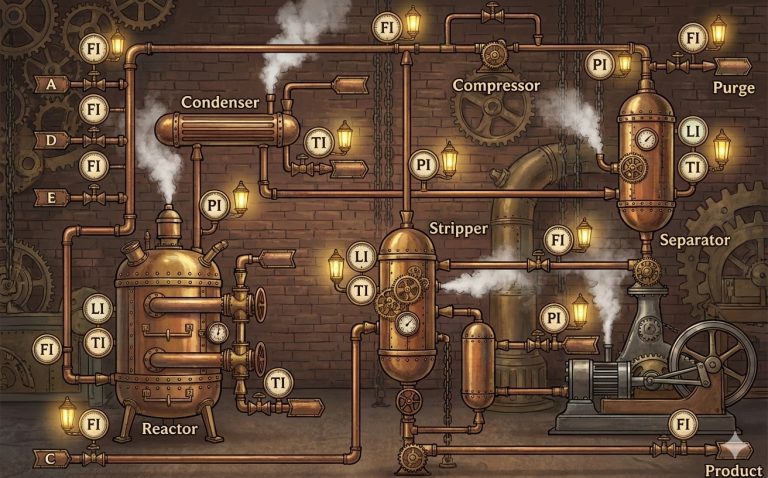
The Tennessee Eastman Process simulator is an interactive simulation and dashboard for the classic Tennessee Eastman chemical process benchmark. It provides a web-based interface to run and visualize dynamic simulations of the process, including the ability to introduce disturbances and monitor process variables in real time. The underlying software is a Python-based simulator (with optional Fortran acceleration) for research and teaching applications in process control, fault diagnosis, and chemical engineering systems.